Design
Data Transport between Producers and Consumers.
Current Data Transport Problems
- Adhoc log aggregation
- Duplicate data transfer
- Tightly coupled - brittle
- No Reliability Guarantees
- Network glitches lead to huge backlog
- High peak bandwidth requirement
- No support or different data paths for near real-time use
Goals
- Capability to transport event data between distributed sub-systems in reliable, efficient, scalable and uniform way for batch as well as near real-time consumption.
- Decouple data consumers from producers
- Savings on Network Bandwidth
- Reduce peak network requirements due to bulk data transfers in spurts.
- Minimize Duplicate data transfers across WAN
What Conduit is NOT ?
- Filtering/transformation layer
- Data is delivered in raw format as being produced
- Data Store
- Consumers are expected to consume the data within certain SLA, after which ALL data is purged
- Batching semantics
- Consumer decide their own batching semantics –Same data stream can be used by multiple consumers with different needs
Technology Evaluation
Details on Scribe setup/scenarios/usecases - ScribeArch
Design
Scribe Agents on each producer node. Producer application log messages using API which will write to the local scribe agent. Local scribe agent forward message to Scribe collectors. Scribe collectors writes to HDFS. Consumers pull data directly from HDFS.
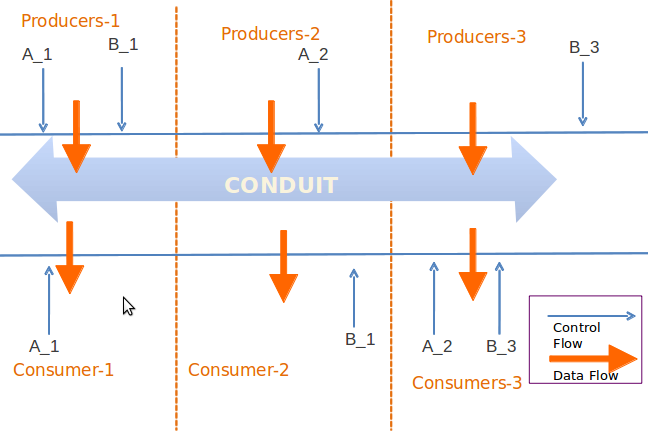
Producer-1, Producer-2 and Producer-3 are the producers of the Conduit and Consumer-1, Consumer-2 and Consumer-3 are the consumers of the Cconduit.
Producer-1 publishes messages to A_1 and B_1 categories to conduit, Producer-2 publishes messages to A_2 category and Produce-3 publishes the messages to B_3 caterogty/stream. Consumer-1 is only pulling the data from only A_1 stream, Consumer-2 is pulling the data from B_1 and Consumer-3 is pulling the data from A_2 and B_3 streams.
Salient Features
- Data compression: All data is kept in compressed form in HDFS. All cross dc transfers are of compressed data.
- Data merging: Merging of local streams from multiple data-center into the single Hadoop cluster closer to the consumer.
- Mirroring: Mirroring of merged data streams into another Hadoop cluster. Enabling BCP.
- Data retention: Manage data retention in the cluster.
